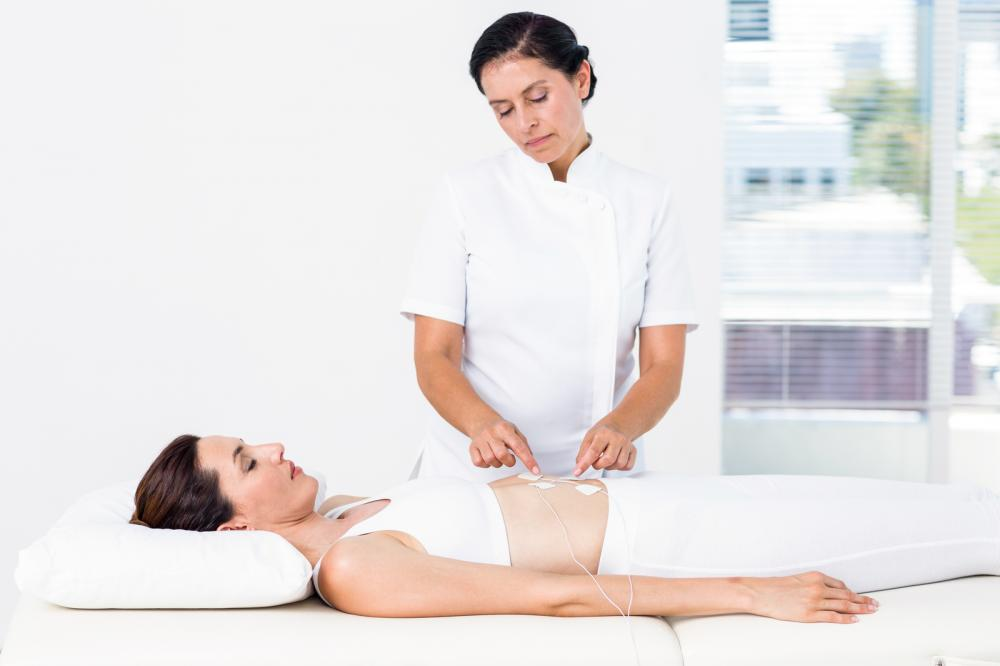
Types of Electrical Stimulation Used In Physical Therapy
One of the modalities of physical therapy used in chiropractic is electrical stimulation. Electrical stimulation is used to regain muscles’ contraction abilities. When your muscles cannot contract, you can experience pain, weakness, and a decreased ability to function properly. You might also deal with limited muscular movement.
Electrical stimulation can be beneficial in conditions of tendonitis, post-surgical pain, lower back pain, bursitis, muscle weakness, or loss of movement control.
If you’ve been experiencing any of the above conditions, your chiropractor might advise you to undergo electrical stimulation. There are many different types of electrical stimulation based on your condition:
1. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation, also known as TENS, is a type of electrical stimulation used to decrease chronic pain.
TENS can alter or interrupt the pain signals traveling to the brain from affected tissues. It is performed with the help of electrified electrodes placed on the affected muscle, which alters pain signals traveling to the brain.
2. Russian Stimulation
Post-surgery or post-injury pain can be intolerable; you might need to visit your chiropractor. After the surgery or a serious injury, you might also experience muscle weakness and an inability to move comfortably.
To restore muscular movement, your chiropractor might recommend Russian Stimulation.
It uses electricity to generate contraction in the muscle by force. The electricity is applied to the affected body part for 10 seconds at an interval of 50 seconds. The entire process may go on for 10 minutes.
3. Interferential Current
Typically, a crisscross pattern of four electrodes is used for interference current. This results in “interference” between the currents passing between the electrodes, hence the name.
Physical therapists and chiropractors use this type of electrical stimulation to improve blood circulation in injured tissues. IFC is more or less similar to TENS, but in this method, current can be controlled and is specifically targeted to areas that are experiencing the most pain.
4. High Voltage Electrical Stimulation
Physical therapists use high Voltage Stimulation to decrease pain and enhance circulation in the injured tissues. High voltage is known to speed the healing process by changing the type of cells around the wound.
5. Iontophoresis
Iontophoresis is an electrical stimulation technique used to permeate the skin with medicines. Medications like dexamethasone can be used to lessen pain and discomfort by reducing inflammation and swelling. Medications used in iontophoresis can be utilized for more than only treating scar tissue and reducing calcium deposits.
6. Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
In the same way that Russian stimulation is used to strengthen muscles, neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) can do the same. As part of their treatment for patients recovering from surgery or injury, physical therapists often employ NMES to facilitate healthy muscle contractions. Muscle re-education techniques like this can speed up a patient’s recovery from an accident or surgical operation.

Advanced Chiropractic Care Services In Kentucky
If you’re wondering, “where can I find electrical stimulation physical therapy near me?” your search ends here. Shelby County Chiropractic in Shelbyville, Louisville, KY, uses electrical stimulation to relieve patients of acute pain and restore muscular movement.
Our founders, Dr. James Stapleton DC, and Dr. William Yadon DC, believe in making sure that patients understand the process of electrical stimulation before starting the chiropractic treatment. If you have any questions regarding the techniques used and which therapy is the most suitable for you, get in touch with us today to book your appointment!